Bill Of Lading in Shipping: Importance, Purpose, And Types
If we search the meaning of the term “bill”, it is defined as a printed or written statement of the cost for the goods or services delivered or delivered. The term “lade” means to put the cargo onto a ship or other form of goods carrier.
Land, ocean and air transport are the modes that use lading bills. Like the inland bills of lading for goods transported via roadways or railways, a bill of lading in shipping records the traded goods received on board.
It is a document that establishes an agreement between a shipper and a transportation company for the transportation of goods. The Transportation Company (carrier) issues these records to the shipper.
There are usually two types of bill of lading, the House Bill of Lading and the Master Bill of Lading. An ocean bill of lading indicates a particular carrier through which the goods have been placed to their final destination and the conditions for transporting the shipment to its final destination.
While many confuse the bill of lading with Proof of Delivery, the former is a contract between the owner of goods and freight carrier, while the latter is proof that the goods have reached their destination.
The Importance of Bills of Lading
The carrier need not require all originals to be submitted before delivery. Therefore, the exporter must retain control over the complete set of the originals until payment is effected, a bill of exchange is accepted, or some other assurance for payment has been made to him.
A bill of lading is very important when making shipments to move the cargo or freight from one point or distribution center to the other. On the one hand, it is a contract between a carrier and shipper for the transportation of goods, and on the other hand, it serves as a receipt issued by a carrier to the shipper.
Hence, the bill of lading is considered a legal document which provides all the vital details to the shipper and the carrier to conveniently process the freight shipment through different maritime countries and invoice it correctly.
The original copy of the bill of lading is provided to the carrier, and a copy of the same should also be ascribed to the packaged freight.
A blank bill of lading template can be downloaded from this link here.
Negotiable and Non-negotiable bill of lading?
Negotiable bill of lading: In this type of bill, clear instruction is provided to deliver the goods to anyone possessing the original copy of the bill, which signifies the title and control of the freight. In this type of bill, the buyer/ receiver or their agent has to acquire and present an original copy of the bill of lading at the discharge port. Without an original bill copy, the freight will not be released.
Non-negotiable bill: This type of bill of lading fixes a specific consignee/name of the receiver to whom the freights will be shipped and delivered. It, however, does not itself serve the owner of the goods. Under this bill, the assigned receiver/ buyers can claim the cargo by confirming their identity.
Purpose
The bill of lading document is meant to act as a transport document as evidence of the contract of carriage of the goods. A negotiable bill of lading has the following legal qualities:
- It acts as a piece of evidence for the carriage contract containing the terms and conditions under which the goods transportation will be carried out.
- It represents a receipt which endorses that the carrier has received the cargo as per the contract and the goods are received in good condition.
- It is a document of title permitting the sale of goods in transit and raising financial credit.
- Most local and international systems do not consider a bill of lading as a title document. It provides the right for the delivery to be made to the possessor.
Different Types
Depending on your shipping destination and type of cargo, there are different bills of ladings. They can be classified based on “how it is executed” and “Method of operation”-
Based on execution
1. Straight bill of lading reveals that the goods are consigned to a specified person, which is not negotiable, free from existing equities. It means any endorsee acquires no better rights than those held by the endorser. This type of bill is also known as a non-negotiable bill of lading, and from the banker’s point of view, this type of bill of lading is not safe. This type of bill is prominently used for military cargo.
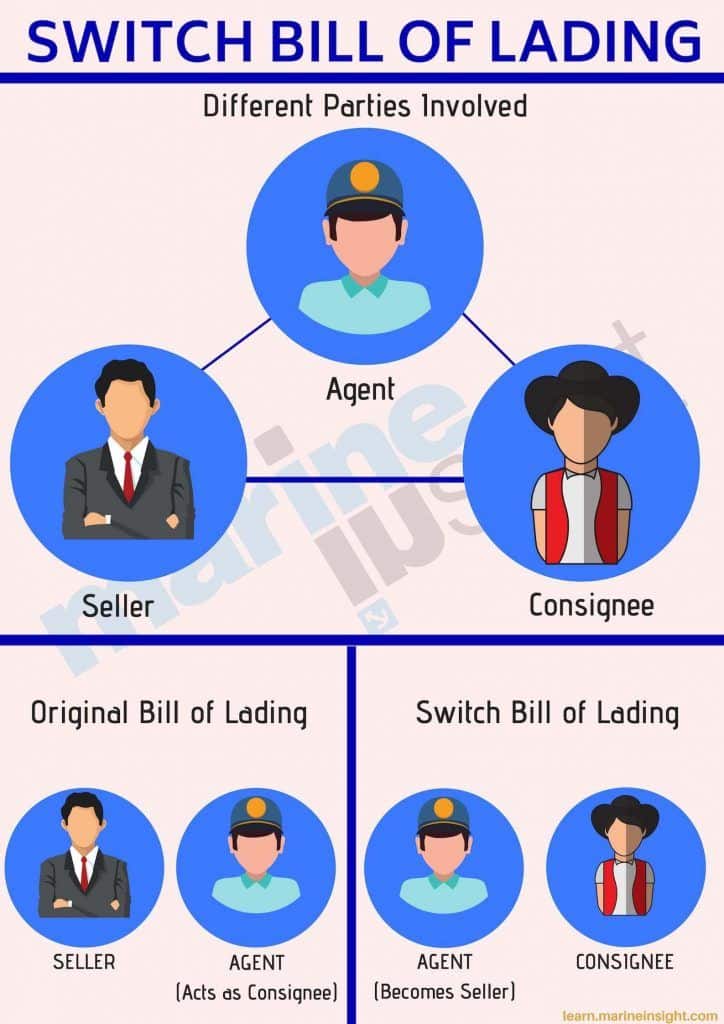
2. Open bill of lading – This is a negotiable bill of lading where the name of the Consignee can be changed with the consignees’ signature and thus transferred. This can be transferred multiple times. A switch bill of lading is a type of open bill of lading.
3. Bearer bill of lading is a bill that states that delivery shall be made to whosoever holds the bill. Such a bill may be created explicitly or an order bill that fails to nominate the Consignee, whether in its original form or through an endorsement in blank. A bearer bill can be negotiated by physical delivery. They are used for bulk cargo that is turned over in small amounts.
4. Order bill of lading is the bill that uses express words to make the bill negotiable. This means that delivery is to be made to the further order of the Consignee using words such as “delivery to A Ltd. or to order or assigns. The cargo is only delivered to the bona fide holder of the lading bill, which must be verified by an agent who issues the delivery order and the verified bill of lading. The order bill of lading:
– is the most modern type of bill, which is widely used all over the world
– ensures the safety of delivery of cargo to a bonafide holder of B/L
– Since the ship visits several foreign ports where the language, practice, and procedures may differ, the master might be inconvenienced during the cargo delivery. People might fraudulently collect the cargo.
– To overcome this difficulty and avoid future cargo claims and litigations, the Consignee or the holder must surrender the bill of lading to the ship’s agent at the discharge port, who will verify the genuineness of the bill of lading. When satisfied, the agent will issue a delivery order and the verified bill of lading. Now, any person can collect the cargo from the ship by surrendering the bill of lading and the delivery note to the ship.
As the bill of lading is made to “to order” of the Consignee, it is a negotiable instrument of title. This means that the ownership of the bill of lading can be transferred from one person to another by authorising the signature and delivery of the bill of lading.
All goods which have not been paid in advance and are shipped under “To order” of the bill of lading can be categorised into two types:
- To Order, Blank Endorsed: not consigned to any named party but ‘To Order’ of the consignor, with the intended – Consignee’s name given under ‘notify party.’ The consignor must stamp and sign (endorse) this B/L so its title can be transferred.
- To Order, Bank: consigned to a bank with the intended Consignee’s name under ‘notify party.’ The bank endorses the B/L to the intended Consignee against payment of (or a pledge to pay) the amount of the accompanying bill of exchange. ‘To Order’ B/Ls are used commonly in the letter of credit transactions and may be bought, sold, traded, or used as security for borrowing money from banks or other lenders.
Based on the Method of Operation
- Received for shipment bill of lading–This bill is sent from agent /charterer to shipper. The endorsement of this bill ensures that the carrier has received goods but does not confirm it is onboard the assigned vessel.
- Shipped B/L – This bill of lading is Issued when cargo is loaded on board. It binds the shipowner and the shipper directly.
- A clean bill of lading states that the cargo has been loaded on board the ship in apparent good order and condition. Such a bill of lading will not bear a clause or notation which expressively declares a defective condition of goods and/or the packaging. The opposite term is a soiled bill of lading. It reflects that the carrier received the goods in anything but good condition.
- Through B/L – This bill of lading is a legal document allowing direct cargo delivery from point A to point B. The bill provides transportation of goods both within domestic borders and through international shipment as it serves as a receipt of the cargo, a contract of carriage, and sometimes title for the products as well
- Combined transport B/L – This bill gives information about cargo transported in large containers by sea and land, i.e. through multi-model transport.
- Dirty bill of lading: If the shipowner objects to “the condition of the cargo are in good order”, they can include a clause thereby causing the bill of lading to be “claused or dirty” along with the remarks as per the finding of the cargo condition. E.g. torn packing, broken cargo, shortage in the quantity of the goods etc.
Related reading: What are container ships?
Sets of Bill of Lading
This is an old practice where the bills are signed in the sets of three originals to facilitate the goods are timely delivered even when the original is lost. They are stated as the first original, second original, and third original on top of the bill. A duplicate copy with the stamp – “Non-negotiable” may also be distributed.
The master will sign the original bill of lading, and when the master of the agent signs the three-bill of lading, all other copies are considered void. This clause is written on the bill of lading supplied in sets.
This is why the bank, negotiating a letter of credit covering the cargo, will always ask for the full set of B/Ls. This prevents other B/L holders from legally claiming the cargo before the bank does.
Bill of lading as Contract Of Carriage
The contract between the carrier and the shipper is already created before issuing the bill of lading when the cargo is loaded on the ship. This is done to safeguard the shipper in case the cargo is damaged before loading it on board the vessel and to help the shipper in the claim process. For the carrier and the Consignee, the bill of lading will act as the actual contract of carriage.
The popularly used conventions and rules which cover the contract of carriage for carrying goods by sea :
– Hamburg Rules
– Hague Rules
– US COGSA
The convention governing the carriage contract is usually stated on the first page of the bill of lading. Upon booking space for shipment by the Consignee, the carrier sends a booking confirmation which states Clauses sent by the carrier. It will indicate the terms and conditions governing the booking and carriage contract.
Contents of Freight Bill of Lading
The bill of lading comprises the following details:
- The complete name and official address of the receiver and the shipper.
- The Purchase order numbers, special reference/ invoice or reference numbers, and special instructions to help the shipper and the Consignee release the goods for pickup or are accepted at delivery.
- The date of the pickup acts as a reference to track the freight.
- The description of items includes the number of units being shipped, NMFC freight class, the weight and dimension of the products, and the nature of the cargo being carried, i.e. dangerous goods etc.
- If the goods are hazardous, the Department of Transportation hazardous material designation is tagged, and it is cited on the bill to follow particular rules and requirements when shipping.
- The packaging details include crates, pallets, cartons, pills, drums etc.
- Any special notes or instructions for the carrier.
Bill of Lading Tracking:
Different companies use different forms of bill of lading, making tracking challenging unless the carrier provides a specific tracking service. A few companies tie up with the shipping carriers to track the bill of lading for easy trade.
However, these precautions must be taken before signing the bill of lading.
Electronic Bills of Lading:
With the modernisation of the shipping industry as a whole, the bill of lading is also modernised to the electronic bill of lading to solve the issues occurring while using a paper bill of lading under the latest iteration of the International Group of P&I Clubs. The problem faced when using a paper bill of ladings are:
The paper bill uses printed bills of lading which are both costly. The bill has to be couriered, which is an additional cost.
– The slow movement of the paper-based bill of lading.
– Carriers are obligated to release the goods on the production of an original bill of lading, which will slow the process if not received in time.
– The paper bill can be forged, and delivery of goods against a forged bill of lading will lead to a huge loss
Related Reading: A Guide To Verified Gross Mass In Shipping

Advantages of Electronic Bill of Lading:
- As there are no papers involved, it saves paper cost as well as the cost involved in sending the paper to a different destination by courier
- The electronic bill of lading can be transmitted instantaneously worldwide in the presence of an internet connection, enabling quick trade and ease of multiple ownership transfers during the cargo carriage.
- If any modifications are required in the bill, they can be made quickly and cost-effectively compared to the bill of lading paper system.
- If the electronic bill of lading system is drawn correctly, such as introducing audit trials, PIN, electronic signature etc., it will be difficult to commit fraud.
Problems with the Electronic Bill of Lading
It is possible to negotiate and transfer the possession of the paper bill as it is evidence of the title of the goods. However, this is not automatically the case with e-bill.
(Source – A paper bill of lading is a title document, enabling it to be negotiated and transferred as possession of the bill is evidence of title to the goods. This is not automatically the case at law with an e-bill)
If the electronic bill system is not secured, it can be hacked, and the details can be manipulated as per the hacker’s convenience, leading to fraud and loss of cargo.
Implementation of an electronic bill system across the industry needs consent from all the stakeholders, which will take time.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the purpose of a bill of lading?
A bill of lading is a contract issued by a transportation company to a shipper that gives out the quantity and types and specifies the destination of goods being shipped. It is also a receipt of shipment and prevents the goods from being robbed while transported.
2. Who is responsible for the bill of lading?
It is a legal document issued by a carrier to a shipper. It must be signed by an authorised representative from the carrier, shipper, and receiver.
3. Why is it called a bill of lading?
The term ‘lading’ means loading and is derived from the old English word hladan. Lading refers to loading cargo onboard a vessel.
4. What is the main purpose of a master bill of lading/MBL?
MBL is issued by a carrier and represents the legal contract for the carriage of goods from one destination to another. Once the carrier receives the goods, it would issue the document to the party that booked the freight, the freight forwarder or shipper.
5. When was the bill of lading invented?
According to Researchers and Historians, the earliest bills of lading date back to Spain in 1544. Before the commencement of air travel, sellers would send cargo to distant buyers via waterways.
You may also like to read
- What is Blind and Double-Blind Shipment?
- What is Switch Bill of Lading?
- What Precautions Should be Taken Before Signing the Bill of Lading?
- Rotterdam Rules – Redefining and Introducing the Electronic Bill of Lading
- What is Seaway Bill in Shipping?
- NOTIFY PARTY in Shipping – Everything You Wanted To Know
Disclaimer: The author’s views expressed in this article do not necessarily reflect the views of Marine Insight. Data and charts, if used in the article, have been sourced from available information and have not been authenticated by any statutory authority. The author and Marine Insight do not claim it to be accurate nor accept any responsibility for the same. The views constitute only the opinions and do not constitute any guidelines or recommendations on any course of action to be followed by the reader.
The article or images cannot be reproduced, copied, shared or used in any form without the permission of the author and Marine Insight.

Great article. I work for a company that ship merchandise to department stores and one of my job is to verify and transmit an ASN. An ASN is an advance shipping notice. It is similar to an BOL but it is transmitted in an advance to the customer so they know what merchandise, order, PO#, sku, etc… they will receive (before the box or carton arrives in their docking station).
We also submit a BOL (manually created) to the trucker who receive the cartons and load it on his truck.
Dears,
I would like your positive guide on when and why we need “Switch Bill Of Lading ?
Please guide me in a easy way with some examples since I am a newcomer in Logistics Field.
Thanks & regards
Touseef –
@ Touseef-
We will bring some information on your suggested topic soon.
Thank you
carrier issued 3 orignal. and if surrnder one orignal to carrier, what will be tatus of other 2 orignals? pls be guided
Does anyone know where I can find a blank bill of lading to fill out?
Check this link for the attachment- https://forums.marineinsight.com/forum/nautical-science/1613-what-is-bill-of-lading
Who is responsible for delivery on a “door delivery” bill of lading shipment?
Dears
I want know full process of import-export documentation, if,it is possible, update on my email.
Thanks
@Jitendra: Please use our forums – https://forums.marineinsight.com
Hey!
I am just starting in this industry and this article really helped me out. I was wondering if you could also enlighten me with some knowledge of Bill Of Lading.
Thanks,
Bryan Snyder
Nowadays, various types of BOL has been presented in this market industry, the most common BOL are Master Bill of lading (MBOL) and House Bill of lading (HBOL). Identify the difference mechanism between MBOL and HBOL when it involves with Letter of Credit (L/C) functions.
1.Please help me get the similarities between sea waybill and Bill of lading.
2.explain with an examples how five of the 17 exceptions build upon the common law exceptions applicable to every carriage
a.Act of God
b.Queens enemies
c.Inherent vice
d.fundermental breach of the shipper
3.briefly analyzed the situation under which a carrier will not be able to rely on a listed exception.
Please help me solve this three questions
We are glad it came useful to you Bryan
I am Mehedi Hasan. I am a commercial officer . one invoice to three original copy of b/l(bill of leading ),so its a great news for export inport business & shipper.
The most common BOL are Master Bill of lading (MBOL) and House Bill of lading (HBOL). Identify the difference mechanism between MBOL and HBOL when it involves with Letter of Credit (L/C) functions
HI GOOD DAY.
I am just starting in this industry and this article really helped me out. I was wondering if you could also enlighten me with some knowledge of Bill Of Lading.
HI GOOD DAY,
I am just starting in this industry and this article really helped me out. Thank you for your information.
BEST REGARDS.
ABDUL HADI BUTT
@Abdul/: Glad the content helped 👍